

SAP Production Planning stands as a cornerstone module within the SAP ecosystem. It includes many important functions that help organizations run smoothly and improve the efficiency of the manufacturing process. This module manages essential processes including material planning, capacity planning, production scheduling, goods movement etc. It plays a pivotal role in aligning a company’s production capacity with market demand, enabling organizations to effectively meet their production goals. Furthermore, it seamlessly integrates with other key SAP modules, including SAP Material Management, Quality Management, Financial Accounting and Controlling (FICO), and Plant Maintenance, fostering a unified and efficient management system for enterprises.
Here are the benefits of having a proper ERP system for a manufacturing organization.
With the above considerations in mind, let’s explore key factors to consider when implementing SAP S/4 HANA in your manufacturing environment. This excludes considerations related to change management and project.
Manufacturing industry can be classified into either discrete or process based on manufacturing process and the products. A manufacturing organization can have either process, discrete or combination of both based on the finished and semi-finished products they manufacture.
Discrete manufacturing involves the production of a product through the assembly of components that can be disassembled. You can further assemble the product, enabling the inclusion of multiple subassemblies in the final product. In this industry, the production of materials is continually adjusted in accordance with the order, and their costs are calculated accordingly. Industry example involves Automotive, Electronics, Machineries, Apparel and footwear, etc.
Process manufacturing involves manufacturing of a product by combining or ingredients or raw materials using a specific formula or recipe under specific condition such as heat and pressure. Industry example includes, food and beverage, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, steel etc.
SAP S/4HANA features manufacturing with production orders tailored for discrete industries and manufacturing with process orders customized for process industries, each designed with industry-specific built-in features. Organizations can customize their implementation to meet the requirements when their products encompass both process and discrete features, incorporating both processes and discrete features as needed.
In addition to that SAP S/4 Hana comes with industry specific solutions such as SAP S/4 Hana for Fashion and Vertical business which aims specific requirements of the fashion industry.
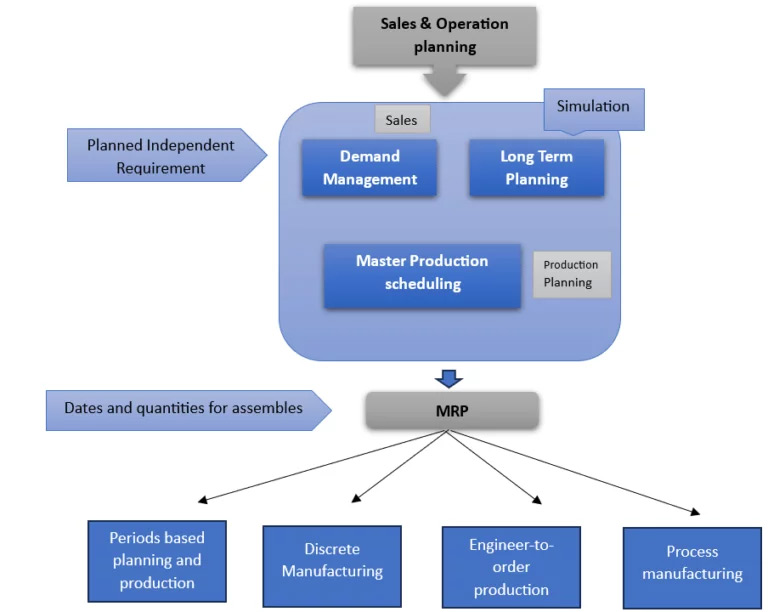
Figure 1: Production Planning and Control
Organizational structure represents organizational units in a hierarchy. In SAP S/4 Hana organization structure contains, manufacturing plants and locations as far as the manufacturing is concerned.
For a manufacturing organization there can be multiple manufacturing locations which are the plants. Plants then can be divided into multiple locations.
There will be several factors including deciding manufacturing facilities as separate plants or virtual plants based on the location proximity and due to financial reasons, such as different inventory valuation requirements, different legal account procedures with each plants having different legal entities etc.
After deciding on the plants, you can determine storage locations, including those for raw materials, production shop floor issuing locations, and finished goods warehouses. In some cases, virtual locations may be necessary to track specific materials or to run material requirement plans separately.
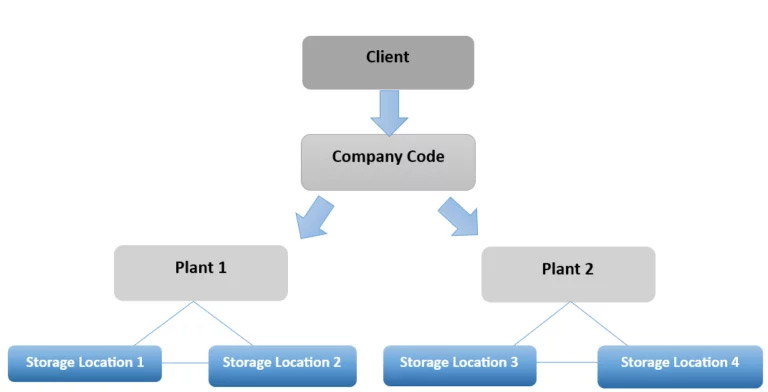
Figure 2: Organization Structure
Organization should consider the following master data aspects to eliminate master data redundancies, ensure production planning, execution and costing to be accurate and efficient.
Organizations should look into below production planning aspects, as implementing real-time monitoring of production processes allows organizations to quickly respond to any disruptions or deviations from the plan, ensuring production stays on track and costs are controlled.
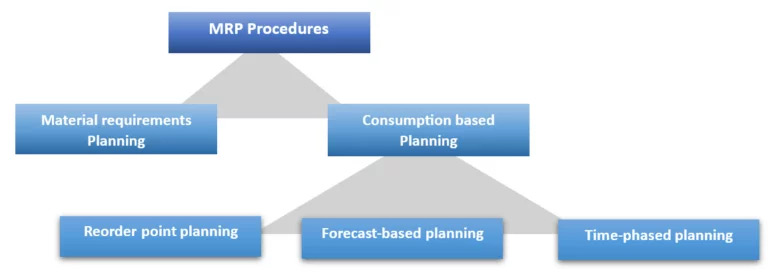
Figure 3: MRP Procedures
Production processes in a manufacturing business could be in the form of Inhouse manufacturing, sub-contracting, external processing, or contract manufacturing. SAP offers best practices with pre-configured process for each production process forms.
In the SAP Production Planning (PP) module, Production Execution refers to the phase in which planned production orders are transformed into actual production activities on the shop floor.
It involves the hands-on activities of producing goods, including tasks such as machine operations, material handling, and quality control. Key aspects of production execution in SAP PP include.
Intellect Consulting, a leading SAP consulting company. Which offers a team of seasoned consultants committed to facilitating a seamless transition to SAP S/4HANA for manufacturing organizations. With our expertise, your business can harness the power of cutting-edge technologies. We help you streamline operations, and inject intelligence into every facet of your processes.
By partnering with Intellect Consulting, you embark on a transformative journey with SAP S/4HANA, positioning your organization to soar to new heights. Join us on this path to innovation, efficiency, and a brighter future for your manufacturing endeavors.